Rubber moulding transforms rubber compounds into reliable components through processes like compression, transfer, and injection. It supports a wide range of industries with products that demand accuracy, flexibility, and long-term performance.
What is Rubber Moulding?
Rubber moulding (also called rubber molding) is a versatile manufacturing process that transforms uncured rubber or elastomeric materials into finished products. It involves placing raw rubber into a mold cavity and applying heat and pressure to cure and shape it into the desired form. Rubber moulding process enables the production of seals, gaskets, grommets, boots, and more, with advantages such as precision, consistency, and the ability to bond rubber to metal.
The Rubber Moulding Process
A typical rubber moulding process involves the following steps:
1. Design and Prototyping: Engineers create 3D CAD models of the part and test prototypes before mass production.
2. Material Selection: Choose from materials such as silicone, EPDM, NBR, or natural rubber depending on performance needs.
3. Mold Design and Production: A steel or aluminum mold is manufactured according to part geometry and production volume.
4. Rubber Preparation: Compounds are mixed with additives and curing agents.
5. Molding Process: Depending on the technique, rubber is shaped by injection molding, compression molding, or transfer molding.
6. Curing: Heat and pressure strengthen the rubber’s molecular structure.
7. Finishing and Quality Control: Parts are trimmed, inspected, and tested for tolerance compliance.
Types of Rubber Moulding
As we mentioned before, there are 3 different types of rubber moulding:
Compression Molding:
Compression molding is a traditional rubber molding method ideal for producing parts with simple to moderate complexity. In this process, preheated rubber is placed into an open mold cavity, which is then closed under pressure. Heat and pressure cause the rubber to fill the mold and cure, typically through vulcanization. Once cured, the part is removed, trimmed, and inspected for quality.
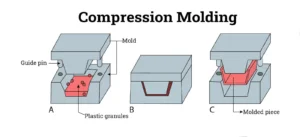
Advantages of Rubber Compression Molding:
- Low Cost: Simple tooling design and reduced production costs with higher volumes.
- Low Maintenance: Easy to clean and repair due to the simple design.
- Material Variety: Handles a wide range of rubber materials without relying on material flow.
- No Gate Vestige: No gate marks on the final product, improving aesthetics and reducing finishing costs.
Disadvantages of Rubber Compression Molding:
- Dimensional Tolerance: Less precise than injection molding, with potential deviations in complex shapes.
- Finishing: Requires additional work to remove flashes and parting lines, adding time and cost.
Applications of Rubber Compression Molding:
- Seals & Gaskets: Used in door/window seals, gaskets, O-rings, and stoppers.
- Shock Absorbers & Protective Parts: Vibration dampers, protective covers, and cable sleeves.
- Consumer & Medical Products: Rubber mats, appliance seals, and medical stoppers.
Transfer Molding:
Transfer molding combines elements of injection and compression molding. Preheated rubber is placed into a chamber (the pot) next to the mold cavity. A plunger forces the rubber into the mold through a runner system and gate. Heat and pressure cure the rubber, and once completed, the molded part is removed, trimmed, and inspected.
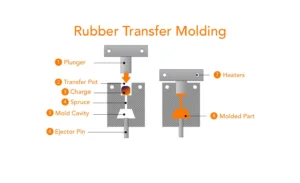
Advantages of Rubber Transfer Molding:
- Tight Tolerance: Provides accurate part geometries with high dimensional precision.
- Metal Bonding: Ideal for manufacturing rubber-to-metal bonded parts, like metal-rubber mounts.
- Large Parts: Can easily accommodate large mold cavities.
- High Cavity Count: Simple preforms are reusable for many cycles, saving time and effort.
Disadvantages of Rubber Transfer Molding:
- High Tooling Cost: Mold complexity increases the initial setup cost due to features like the pot and sprue.
- Finishing: Requires deflashing to remove excess material.
- High Cycle Time: Longer curing time compared to other processes, affecting production speed.
Applications of Rubber Transfer Molding:
- Sealing Components: Gaskets, O-rings, and seals used in automotive, industrial, and electronic applications.
- Electrical & Electronic Parts: Insulators, connectors, and protective covers for electronic devices and wiring.
- Medical Devices: Rubber parts such as stoppers, seals, and diaphragms used in medical equipment.
- Custom Rubber Parts: Engineered components like bushings, dampers, and vibration isolators for specialized uses.
Injection Molding:
Rubber Injection molding is a highly versatile and precise process used to manufacture rubber components, from small, intricate parts to larger, complex shapes. In rubber mold injection, raw rubber is heated to a molten state and injected into a closed mold under high pressure. This forces the rubber to flow into the mold’s details, creating an accurate replica of the part’s shape. Once cooled and solidified, the part is ejected, trimmed, and inspected.
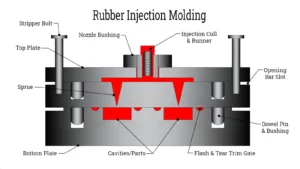
Advantages of Rubber Injection Molding process:
- High Accuracy: Pressurized injection ensures precise filling of the mold, even in intricate details.
- High Mechanical Strength: Parts have strong durability due to ample pressure and curing time.
- No Finishing Required: Minimal defects or excess material, only small parting lines or gate vestiges.
- Quick Process: Optimized control of heat and pressure leads to short curing cycles and faster production.
Disadvantages of Rubber Injection Molding process:
- Material Limitations: Requires flexible, liquid-like rubbers (e.g., silicone, polyurethane), limiting material options.
- High Initial Costs: Expensive tooling and machinery make it less viable for low-volume production.
Applications of Rubber Injection Molding:
- Seals & Gaskets: O-rings, gaskets, and seals.
- Electronic Components: Connectors, insulators, and waterproof parts.
- Medical Parts: Stoppers, seals, and valves.
- Consumer Products: Grips, handles, and protective covers.
Rubber Materials for Rubber Moulding
Rubber molding offers a wide range of material options, each with its own unique properties and suitability for specific applications. Here are some common rubber materials used in rubber molding:
Natural Rubber (NR):It offers excellent elasticity, resilience, and tear resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring high flexibility and durability. It is commonly used in products such as seals, gaskets, tires, and conveyor belts.
Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR): Offers good abrasion resistance and flexibility, commonly used in automotive and industrial applications.
Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR): Known for its oil and fuel resistance, suitable for sealing applications in automotive and aerospace industries.
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM): Exhibits excellent weathering, ozone, and UV resistance, commonly used in outdoor applications and automotive seals.
Chloroprene Rubber (CR): Offers good weather resistance and flame retardancy, used in gaskets, hoses, and industrial applications.
Polyisoprene Rubber (IR) : Produced through the polymerization of synthetic isoprene. Exhibits high tensile strength, tear resistance, and resilience. Suitable for applications requiring a high-purity, resilient rubber material.
Neoprene (CR): A fire-resistant rubber with strong abrasion properties. Used in applications like motor components, shock absorbers, and seals.
Silicone Rubber (MVQ): It offers exceptional heat resistance, flexibility over a wide temperature range, and resistance to aging and weathering. It is commonly used in medical devices, automotive seals, electronics, and kitchenware.
Fluoroelastomers (FKM): Fluoroelastomers, such as Viton®, are highly resistant to heat, chemicals, and oils. They are commonly used in applications requiring exceptional chemical resistance, such as seals and gaskets in the automotive, aerospace, and chemical processing industries.
Fluorosilicone Rubber (FSR): Combines the temperature resistance of silicone with added resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents. Suitable for aerospace and other applications requiring chemical resistance.
Polyurethane (PU): It offers a balance of elasticity, abrasion resistance, and chemical resistance. It is often used in applications such as wheels, rollers, seals, and bushings in industrial and automotive settings.
How to Choose the Right Rubber?
Choosing the right rubber for your application involves considering several key factors:
1. Temperature Resistance: Identify the temperature extremes your product will face. For high temperatures, use heat-resistant compounds like Silicone. For colder environments, choose rubbers that remain flexible in freezing conditions.
2. Environmental Stress: Assess exposure to factors like UV rays, chemicals, or moisture. Weather-resistant rubbers are ideal for outdoor use, while chemical-resistant options are necessary for industrial settings.
3. Physical Forces: Consider the mechanical stresses your product will endure, such as tension, compression, or impact. High-tensile materials like Natural Rubber or Neoprene are suited for demanding applications.
4. Budget: Balance cost and quality. While materials like EPDM are more affordable, they may require more frequent replacements compared to more durable options like Silicone. Choose based on the longevity and performance needed.
Get Our More Material Options
Products and Applications of Rubber Mouldings
Common rubber moulded products include:
O-rings, gaskets, tubing, bumpers, bushings, diaphragms, grommets, isolators, washers, suction cups.

Industry applications include:
- Automotive: Seals, mounts, gaskets.
- Aerospace: High-performance seals, vibration dampeners.
- Medical: Tubing, stoppers, seals.
- Electrical & Electronics: Insulators, connectors, covers.
- Industrial & Agriculture: Vibration isolators, protective seals.
- Food & Beverage: FDA-compliant gaskets and tubing.
Conclusion
Rubber moulding provides a reliable and cost-effective way to create components for diverse industries. At Zhongren, a professional rubber molding company, we specialize in custom rubber mouldings services, offering one-stop solutions from mold to production. Contact Zhongren today to discuss your custom rubber moulding project.





