Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) exists in polyester-based and polyether-based forms. These materials provide elasticity combined with processability through thermoplastic polyurethane injection molding. Are you choosing injection molding as the process for TPU components?
Why TPU is Ideal for Flexible Components?
TPU outperforms materials such as TPE, silicone rubber, and standard thermoplastics in flexible applications. It delivers elongation rates up to 500 percent, which supports repeated stretching without permanent deformation. Abrasion resistance exceeds that of nylon by three times, extending service life in high-friction environments. Chemical stability resists oils, greases, and solvents, maintaining integrity in industrial settings.
Low-temperature performance remains consistent down to minus 40 degrees Celsius, ensuring flexibility in cold conditions. Hydrolysis resistance in polyether-based grades prevents degradation in humid environments. Biocompatible variants meet medical standards for skin contact devices. Recyclability allows regrinding of runners and defective parts, reducing waste in TPU material injection molding.
Compared to TPE, TPU provides superior oil resistance. Against silicone, it offers easier processing and lower cost. Versus vulcanized rubber, TPU enables faster cycles in TPU molding without secondary curing.

How to Select the Right TPU Material?
Choosing the appropriate TPU for thermoplastic polyurethane injection molding is critical to the performance and longevity of the part. TPU materials vary in hardness, elasticity, and thermal characteristics, which influence their suitability for specific applications.
| TPU Hardness | Flexibility | Wear Resistance | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shore A 60–70 | Very flexible | Moderate | Soft seals, protective covers, flexible tubing |
| Shore A 70–85 | Moderate | High | Shoe soles, vibration dampers, gaskets |
| Shore A 85–95 | Firm | High | Industrial wheels, bushings, load-bearing components |
| Shore D 25–50 | Rigid | Very high | Structural components, mechanical parts, automotive fittings |
Key Techniques for Successful TPU Injection Molding
Achieving high-quality parts in tpu injection molding requires careful control of processing parameters. Key factors include:
- Choose the Right TPU Grade: Selecting the proper grade based on flexibility, hardness, wear resistance, and operating conditions ensures durability and optimal performance.
- Proper Material Preparation: Drying and conditioning TPU pellets removes moisture and prevents defects like splay or voids during injection. Proper preparation ensures consistent melt quality and reduces material degradation.
- Good Mold Design: Optimized mold design supports uniform flow, consistent cooling, and easy demolding. Key factors include gate placement, runner system, venting, wall thickness uniformity, and adequate draft angles. Good design minimizes warpage, shrinkage, and surface defects.
- Optimal Processing Conditions: Maintaining the correct barrel and mold temperatures, injection pressures, screw speeds, and cycle times ensures complete filling, minimizes shear stress, and maintains dimensional stability. Adjustments may be needed for part thickness and geometry.
- Post-Processing: After molding, parts may require trimming, deflashing, or surface finishing. Additional treatments like thermal stabilization or coating can improve wear resistance, chemical resistance, and aesthetics, especially for outdoor or industrial applications.
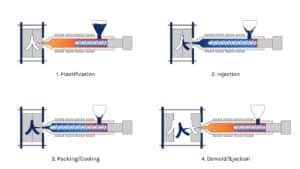
TPU Overmolding and Insert Molding Considerations
TPU overmolding and insert molding involve multi-material parts where TPU is used as the secondary (or surrounding) material over a substrate, or as an insert around a pre-formed part. Key considerations cover material compatibility, processing, substrate preparation, and mold design to ensure strong bonding and void-free parts.
Overmolding TPU onto substrates (like nylon, ABS, metals) requires careful attention to bonding, substrate temperature, and mold design to manage shrinkage, flash, and gas-related defects.
Insert molding with TPU involves ensuring good interface bonding between the insert and TPU, controlling moisture, and selecting compatible materials to avoid delamination or poor adhesion.

TPU Injection Molding Design Considerations
Designing high-quality TPU injection molded parts requires careful consideration of material properties, mold geometry, and processing behavior. The following summarize key considerations:
- Wall Thickness: TPU’s flexibility allows it to fill thinner walls more easily than rigid thermoplastics. Uniform wall thickness is critical to prevent warping, ensure part strength, and maintain dimensional stability. Thinner walls reduce material use and weight, while thicker sections may require reinforcement to preserve mechanical integrity.
- Draft Angles: TPU tends to stick to mold surfaces, and proper draft reduces ejection force, minimizes surface defects, and shortens cycle times. While TPU’s elasticity allows for slightly lower draft angles than other plastics, optimized angles improve uniformity and overall quality.
- Rib Design: Ribs enhance structural strength and resistance to twisting, but they must be carefully proportioned. Rib thickness should be less than the wall thickness, and spacing should allow material flow and flexibility. Rounded corners and stress-aligned rib placement help prevent sink marks and warping while maintaining mechanical performance.
- Material Flow: Proper flow management ensures complete cavity filling without voids or internal stresses. Gate location, flow channels, and injection speed must be balanced to accommodate TPU’s low viscosity and high elasticity.
- Cooling Considerations: TPU has low thermal conductivity, so mold temperature and cooling channel design must be carefully controlled. Controlled cooling improves mechanical properties, reduces residual stress, and ensures consistent cycle times for reliable production.
- Shrinkage and Overmolding: TPU exhibits higher shrinkage than many thermoplastics. Tool design should account for this to achieve precise dimensions. In overmolding applications, substrate compatibility and adhesion must be considered to ensure strong bonding and long-term performance.
- Part Size and Geometry: Minimizing part size where possible reduces weight and improves strength. Complex geometries should consider flow paths, ejection feasibility, and stress distribution to ensure functional and aesthetic quality.
Post-Processing of TPU Components
Trimming and Deburring: After molding, TPU parts often have excess material or minor imperfections. Trimming removes flash or unwanted sections, while deburring smooths sharp edges.
Surface Finishing: Surface treatments enhance both aesthetics and functionality. Polishing or buffing creates smooth surfaces, while painting, pad printing, or laser marking can add color, branding, or detailed information.
Annealing for Stress Relief: TPU parts may retain internal stresses due to uneven cooling or differential shrinkage, particularly in thick-walled components or those with inserts. Annealing relieves these internal stresses, improving dimensional stability and mechanical performance.
Conclusion
TPE injection molding offers many advantages buto also has many challenges. Cooperate with experienced manufacturer will solve the challenges and get high quality flexiable durable and high precision TPU components. Contact Zhongren and get a professional TPU injection molding solution.





