ABS injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process that shapes Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) into durable, precise plastic components. In this article, we will explore how ABS injection molding delivers customized plastic products.
What is ABS Plastic?

ABS, or Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene, is a thermoplastic polymer revered for its balance of strength, affordability, and processability. Formed by copolymerizing three monomers—acrylonitrile for chemical resistance and heat stability, butadiene for impact toughness, and styrene for surface gloss and ease of molding. With a density of 1.04-1.06 g/cm³ and a shrinkage rate of 0.4-0.9%, it performs reliably from -40°C to 80°C. It resists acids, alkalis, and wear, making it ideal for indoor applications like electronics or appliances. However, ABS plastic injection is sensitive to UV light, which can cause yellowing without stabilizers.
Grades of ABS Plastic
The ABS injection molding process supports various grades tailored to specific needs. Common grades include:
- High Impact ABS
- Medium Impact ABS
- Low Impact ABS
- Flame Retardant ABS
- Heat-Resistant ABS
- Transparent ABS
- Food-Grade ABS
- Glass Fiber-Reinforced ABS
| Grade | Impact Strength (kJ/m²) | Heat Deflection Temp (°C) | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Impact ABS | >39 | 85-95 | Helmets, Luggage |
| Medium Impact ABS | 22-25 | 85-95 | Appliances, Auto Parts |
| Low Impact ABS | 16-18 | 85-95 | Glossy Consumer Goods |
| Flame Retardant ABS | 20-30 | 90-100 | Electronics Housings |
| Heat-Resistant ABS | 18-25 | >110 | Engine Components |
| Transparent ABS | 15-20 | 85-95 | Optical Components |
| Food-Grade ABS | 20-25 | 85-95 | Food Containers |
| Glass Fiber-Reinforced ABS | 25-35 | 95-105 | Structural Parts |
Why Use ABS in Injection Molding?
The following explains why ABS plastic injection molding stands out:
- High Efficiency, Low Waste: ABS molding boasts cycle times as low as 20 seconds, with scrap rates below 1%. For high-volume production—like millions of LEGO bricks—it’s a game-changer.
- Design Flexibility: Its low viscosity allows ABS injection moulding to fill complex molds, enabling intricate geometries or embedded metal inserts for added strength.
- Mechanical Durability: With impact strength up to 39 kJ/m², ABS plastic molding resists cracks and chemical corrosion, outperforming many plastics at half the cost.
- Aesthetic Versatility: ABS moulding supports glossy finishes, vibrant colors, and electroplating, meeting demands from matte appliance panels to shiny gadget casings.
- Cost and Energy Savings: Melting at ~220°C, ABS injection reduces energy use by up to 30% compared to high-melt plastics, lowering per-unit costs.
- Recyclability: Fully recyclable and non-toxic, ABS plastic injection molding aligns with sustainable manufacturing trends.
Disadvantages of ABS Injection Molding
No material is flawless, and ABS plastic injection has limitations. Understanding these ensures better outcomes:
- UV and Weather Sensitivity: Prolonged sunlight exposure degrades ABS injection molding parts, causing brittleness.
- Hygroscopic Nature: ABS absorbs moisture, risking bubbles or warping in ABS moulding.
- Limited Heat Stability: Softening above 80°C, ABS plastic molding isn’t ideal for high-heat environments.
- Fatigue Weakness: Repeated stress can crack ABS injection parts. Add ribs to distribute loads and enhance durability.
- High Initial Mold Costs: ABS injection molding process requires pricey molds, making it less economical for low volumes.
ABS Injection Molding Process
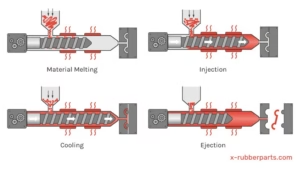
The ABS plastic injection molding process involves several streamlined steps designed to maximize efficiency and product quality:
- Drying: Due to its hygroscopic nature, ABS resin pellets are dried at around 80-85°C to remove moisture that could cause defects.
- Feeding: Dried ABS pellets are fed into the injection molding machine hopper.
- Melting and Injection: The pellets are heated to a molten state and injected at high pressure into the mold cavity.
- Cooling: The molten ABS solidifies as the mold is cooled evenly.
- Pressure Holding and Ejection: Apply holding pressure to optimize density, then eject parts via pins.
- Post-Processing and Inspection: Trim flash, verify dimensions, and prepare for the next cycle.
Design Guidelines for ABS Plastic Injection Molding
Optimizing ABS injection requires a precise design to avoid defects and enhance performance. Important design considerations for ABS injection molding include:
Wall Thickness: Maintain uniform thickness generally between 1.5 to 3 mm to promote even cooling and reduce warping or sink marks.
Draft Angle: Use 0.5-2° draft for smooth ejection; increase to 3° for textured surfaces to avoid scratches.
Injection Pressure: Use appropriate injection pressures to ensure complete mold filling without causing flash or sticking.
Cooling Channels: Design molds with well-distributed cooling channels for uniform temperature control, enhancing dimensional stability.
Nozzles and Runners: Use 6-8 mm diameter nozzles, keep runner length <1 mm, and employ multi-gate systems for even flow.
Avoid Thickness Transitions: Avoid thickness transitions >25%; for thin walls, increase injection pressure; for thick sections, add ribs (height <70% of wall thickness).
Ribs and Fillets: Limit rib height to <4 mm; use fillets with radius >0.25 times wall thickness to reduce stress concentrations.
Applications of ABS Injection Molding

ABS injection molding serves a broad range of industries due to the material’s versatile properties:
- Automotive: Dashboard panels, door trims, seatbelt components, and bumper parts.
- Consumer Products: Toys such as Lego bricks, keyboard keys, tool housings.
- Construction: Power tool casings, electrical outlet fittings.
- Medical Devices: Housing of blood glucose monitors, inhaler housing, pump housing, ergonomic handles.
Zhongren Custom ABS Injection Molding Services
Zhongren leverages expert knowledge and advanced technology to provide custom plastic moulding service tailored to diverse industrial needs. With strict quality controls and experienced design guidance, Zhongren helps clients maximize the benefits of ABS plastic molding, delivering reliable, high-quality parts on schedule.





